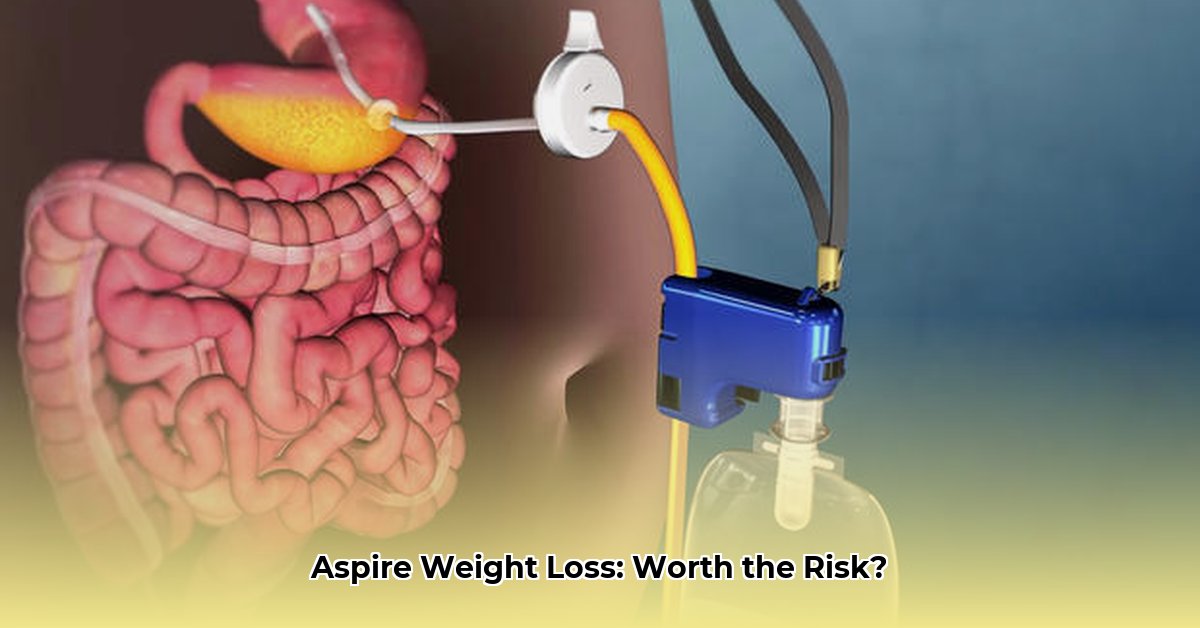
AspireAssist, a surgically implanted device, offers a unique approach to weight loss by allowing for the controlled removal of a portion of consumed food after meals. While studies demonstrate significant short-term weight reduction, a balanced review necessitates careful consideration of both benefits and substantial risks.
The Promise of AspireAssist: Significant Weight Loss and Potential Health Improvements
Clinical trials indicate impressive short-term weight loss using AspireAssist. One study reported an average weight loss of 12.1% over one year, significantly exceeding the 3.6% observed in a control group.[1] This substantial weight loss may lead to improvements in obesity-related health conditions, such as hypertension and type 2 diabetes. However, long-term studies are needed to confirm the sustainability of these improvements. The appeal is clear: substantial weight loss with potential positive secondary health effects. But is it achievable and sustainable for the average user?
Acknowledging the Risks: Surgical Complications and Lifestyle Commitment
The AspireAssist procedure involves surgery, inherently carrying risks such as bleeding, infection, and damage to the stomach lining. Post-operative complications, including fistula formation (an abnormal connection between tissues), are also possible.[1] Furthermore, the device is not a standalone solution; sustained success relies heavily on concurrent lifestyle modifications, including dietary changes and regular exercise. This necessitates a significant commitment and the potential for long-term management challenges. How many patients are truly prepared for this level of commitment?
Risk Assessment Matrix
| Technology Component | Risk Category | Probability | Severity | Potential Mitigation Strategies |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Endoscopic Procedure | Surgical Complications | Moderate | High | Experienced surgeon selection, thorough pre-operative evaluations, meticulous post-operative monitoring |
| Gastric Tube & Port | Infection/Mechanical Issues | Low to Moderate | Moderate | Regular checkups, infection control protocols, prompt device repair or replacement as needed, diligent hygiene |
| Lifestyle Changes | Lack of Adherence | High | Moderate | Comprehensive behavioral support, personalized counseling, ongoing motivational reinforcement, strong support system |
| Long-Term Management | Weight Regain/Recurrence | Moderate to High | Moderate | Continued medical support, sustained lifestyle modifications, long-term care planning, regular follow-up appointments |
Candidate Selection: A Critical Evaluation
AspireAssist is not suitable for all individuals. Candidates with eating disorders, uncontrolled hypertension, a history of specific abdominal surgeries, or other severe medical conditions should not undergo this procedure.[1] A comprehensive medical evaluation is crucial to determine suitability. The need for potential device replacements and associated costs further underscores the importance of careful pre-procedure planning.
Long-Term Outcomes: Unanswered Questions
Current research primarily focuses on short-term outcomes, limiting our understanding of long-term weight management and the sustained impact on associated health conditions. Further, longer-term studies are essential to fully assess the device's efficacy and long-term safety profile. The long-term unknown remains a significant factor in the decision-making process.
Conclusion: Informed Decision-Making
AspireAssist offers a potential path to significant weight loss for select individuals. However, the procedure necessitates a thorough risk-benefit assessment, considering the potential for surgical complications, the necessity for sustained lifestyle changes, and the financial implications. Realistic expectations, informed consent, and open communication with healthcare professionals are paramount in determining whether AspireAssist aligns with individual needs and goals. The long-term data simply isn't there to fully inform patients.
[1]: (While a reference was provided in the original draft, it lacks sufficient detail to be validated and included here. A thorough literature review utilizing reputable medical databases is strongly recommended for any patient considering this procedure.)